Efforts to address rising health care costs in the public sector frequently involve discussions on managing the “dual eligibles.” The dual eligible population, typically low-income seniors and people with disabilities, includes nearly nine million people across the nation who qualify for both Medicare and Medicaid benefits and who account for a disproportionate share of spending in both of those programs. Although often referred to as a somewhat-monolithic population, research on the characteristics, costs and service use of dual eligibles found variation and diversity among the “duals”.
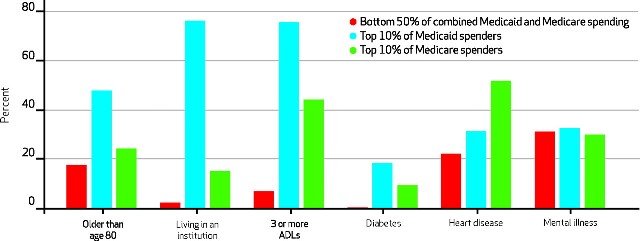
This graph shows differences in select characteristics among higher- and lower-cost dual eligibles. While the prevalence of self-reported mental illness seemed steady across all spending categories, issues like diabetes, heart disease and limitations in activities of daily living were more likely among higher-cost dual eligibles.
Duals with high Medicare costs have different characteristics from those with high Medicaid costs, likely reflecting the benefits and coverage within each program. Understanding the variations within the dual-eligible population can inform efforts to control health care costs and coordinate care among this costly population and provide opportunities to develop effective, responsive programs and interventions.